Building your career is a struggle for everyone in every industry.
It requires a lot of sacrifice, time, and energy.
As an Analyst, you'll have a lot of doors open once you receive that first promotion, or even after the first year or two of experience.
The field you choose to pursue after your Analyst experience depends on what you want to do, where you want to work, and what kind of life you want to live.
This guide was created to give you a high level run-down of all the different fields Analysts tend to pursue in a career.
You are the captain of your career, drive the ship, however, and wherever you please.
All aboard...
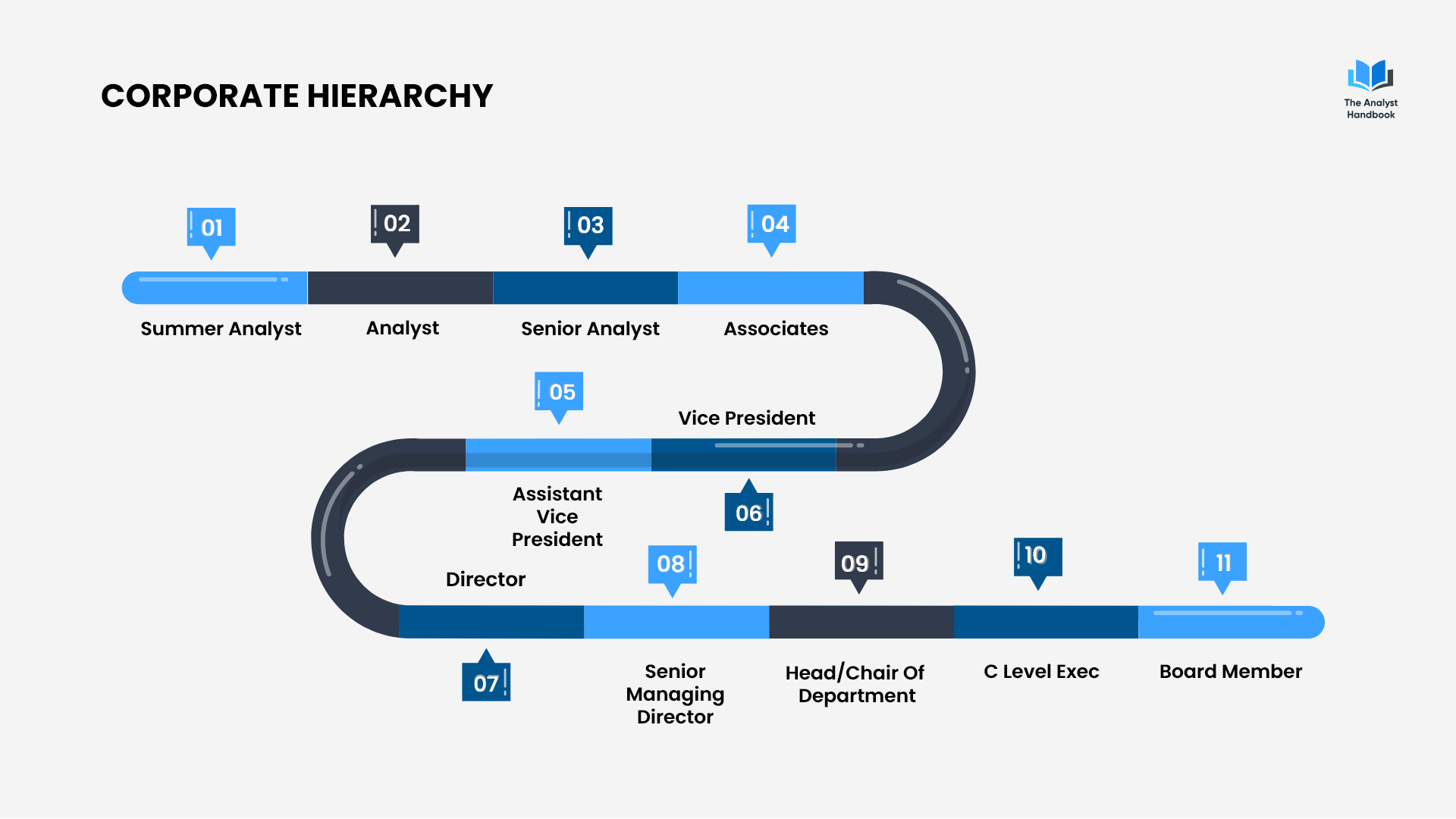
The Corporate Hierarchy
We wanted to give you a quick summary of how the hierarchy of a corporation works.
Most companies where Analysts are present will have some sort of corporate hierarchy similar to this one. You start as an Analyst and work your way up to Associate.
Where the pay is higher, and the responsibilities less tedious.
As you move up the ladder, the tasks will become more exciting, and the pay will grow larger.
Everyone wants to be at the top, but in order to get there, you have to climb the corporate mountain.
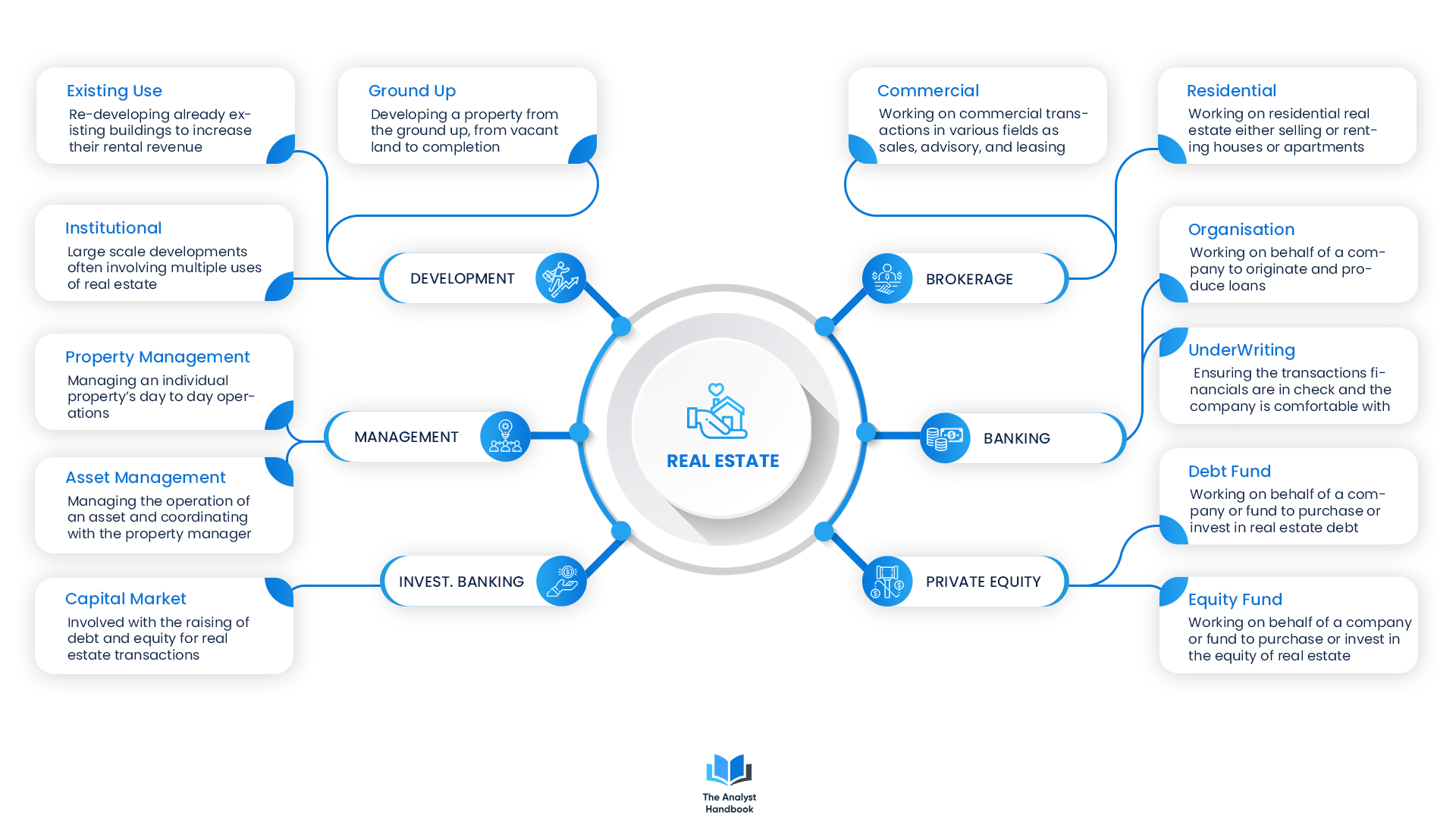
Real Estate
Real Estate is one of the fields Analysts tend to go into. It usually involves some hands-on work with properties and assets, both large and small.
RE Brokerage
Typically a commission based role, or a small salary where you are selling buildings, homes, or properties.
Commercial: Working on commercial transactions in various fields as sales, advisory, and leasing. Typically larger in nature, and more urban or retail-based.
Residential: Working on residential real estate either selling or renting houses or apartments.
National Brokerage: Working at one of the large commercial real estate brokerage shops. Typically, they are specialized by region, asset class, and market.
Team Brokerage: Working on a team of brokers, usually with a senior broker or leader. Usually using a senior broker and their relationships to help them close and execute deals
Individual Brokerage: Working for a one-off a smaller brokerage shop. Usually one main broker, with others around them. More on your own to produce deals and generate income
Note: All of these will involve the buying or selling of Real Estate.
RE Investment Banking
Capital Markets: Working to raise the necessary debt and equity for various real estate deals through alternative funding sources like pension funds, endowments, bonds, and institutional capital funds.
RE Private Equity
Debt Funds: Working on behalf of a large pool of capital looking to be deployed into the debt stack of real estate transactions through bonds, mezzanine tranches, and mortgages.
Equity Funds: Working on behalf of a large pool of capital looking to be deployed into the equity in real estate transactions. Focused on generating value and returns for their capital or investors.
RE Banking
Origination: Working on behalf of a company or team that sources or brings in loans on behalf of a company. Often called production, since their task is to produce deals for the company.
Underwriting: Verifying the transactions comply and meet the standards the company has in place for each market and transaction type. Gathering all the necessary documentation before a loan is funded.
Bridge Loans: Working at a lending company that lends money on real estate transactions that are in complicated or difficult situations.
Fixed-Rate Loans: Working at a lending company that lends money to real estate transactions typically for senior mortgages, or other mortgages involving a fixed down payment.
Agency Loans: Working at a lending company that lends money on behalf of the large federal agencies like Fannie Mae, and Freddie Mac. Guidelines are much stricter, and tougher to comply with, but will always have liquidity.
RE Management (Owner, Operators)
Property Management: Managing the day to day operations of a property. Typically dealing with tenants and the problems or situations that arise at the property (leasing, maintenance, etc.).
Asset Management: Managing the operation of an asset and acting as the liaison between the property manager and the owner, operator. Relaying the information needed to investors, and ensuring the asset is running in a capital-efficient manner.
RE Development
Ground Up: Working at a company that builds properties from the ground up. Typically involves the building of new properties from vacant land or demolished properties.
Existing Use: Working for a company that renovates and upgrades existing properties. Typically involves enhancing an existing property with the hope of increasing the property's income.
Types of RE Development Companies
Family Office: Working at a company that manages the capital of a family or a small pool of investors developing or owning, and operating real estate.
Institutional Developer: Working at a large company that manages institutions capital and develops real estate transactions on a large scale.
Solo Developer: Working at a company that is primarily a one-off developer, or a smaller developer (typically more of a hands on role).
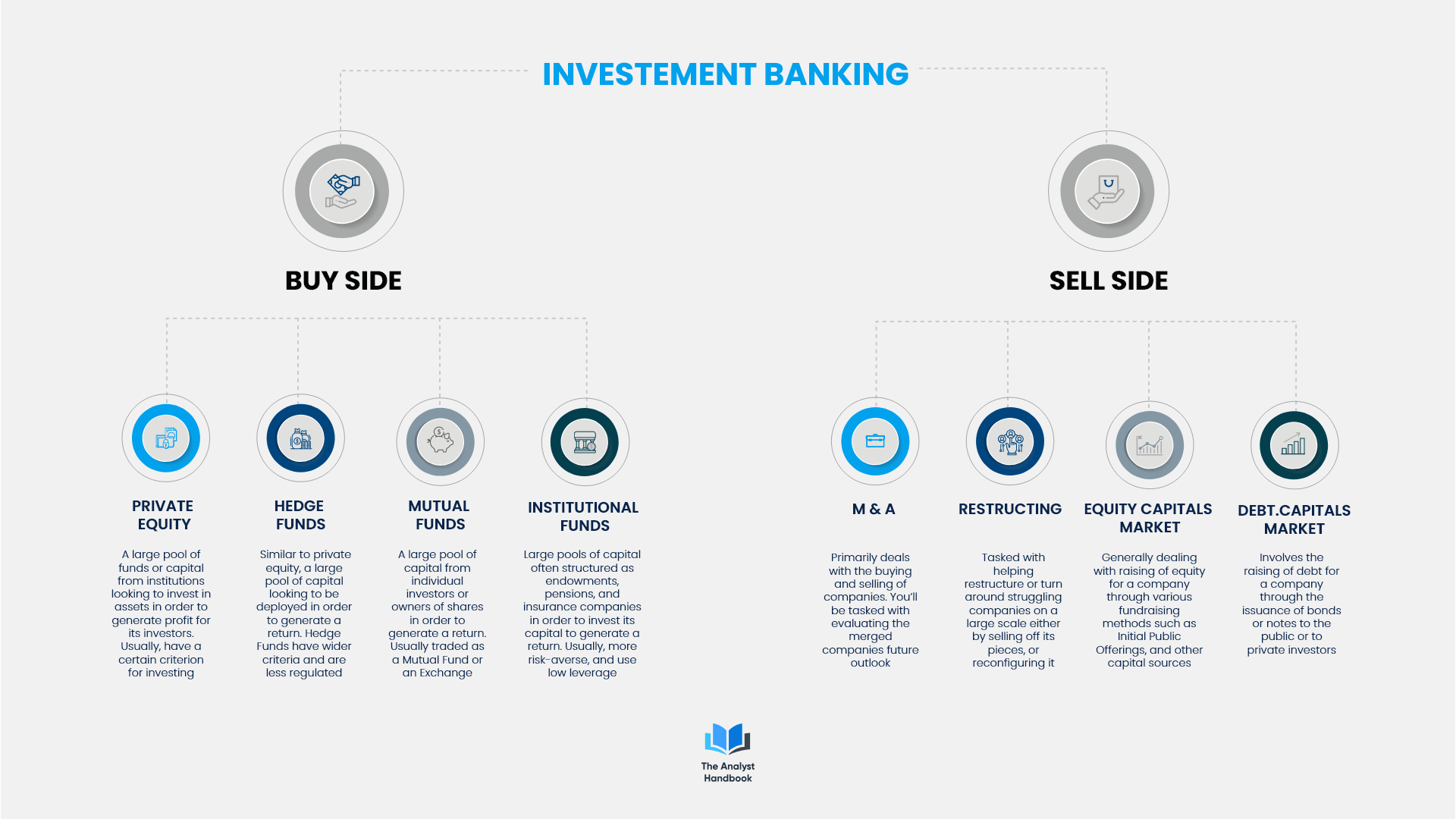
Investment Banking
Buy-Side
Working on behalf of companies or funds looking to purchase and invest capital into various investment vehicles, funds, opportunities, or deals. Private Equity: Working on behalf of a private fund to buy securities, investments, or the deals the investment banks are selling to generate a return (usually with certain criteria or specific asset class).
Hedge Funds: Working at a fund or large pool of capital that is less regulated and has more freedom to invest in riskier asset classes. Similar to private equity, but investing on a larger and wider scale in and not limited to a particular industry or asset class.
Mutual Funds: Working on behalf of a pool of capital from a large group of small investors or part of a securitized fund to make investments or take positions in companies. These companies are often traded on exchanges and referred to as Exchange Traded Funds (trade all day) or Mutual Funds (trade once a day).
Institutional Funds: Working on behalf of a large pension or endowment fund looking to purchase or invest in securities or investments on behalf of a large group of people (teachers, firefighters, etc) to generate yield for their pensions. Usually more risk-averse in nature, and use low leverage.
Sell Side
Working on behalf of a financial institutional looking to sell their products and services (investments, deals, funds, opportunities) to companies, funds, or pools of capital.
Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A): Working in the part of an investment bank involved in the buying, selling, and merging of companies. Heavily involved in evaluating companies and coming to the terms and conditions of a transaction.
Restructuring: Working in the part of an investment bank dealing with the financial engineering, and financial state of a company to try and turn the company around. Usually involves struggling or declining large companies and trying to help restructure their businesses or operations to become more profitable.
Equity Capital Markets: Working at an investment bank helping companies raise equity for deals or transactions primarily through the sale of equity through the issuance of shares to the public, or to placement to private investors (private equity funds, hedge funds, mutual funds, institutional funds).
Debt Capital Markets: Working at an investment bank helping companies raise money for their company or for transactions by issuing debt to the public or to private investors in the form of bonds and securities.
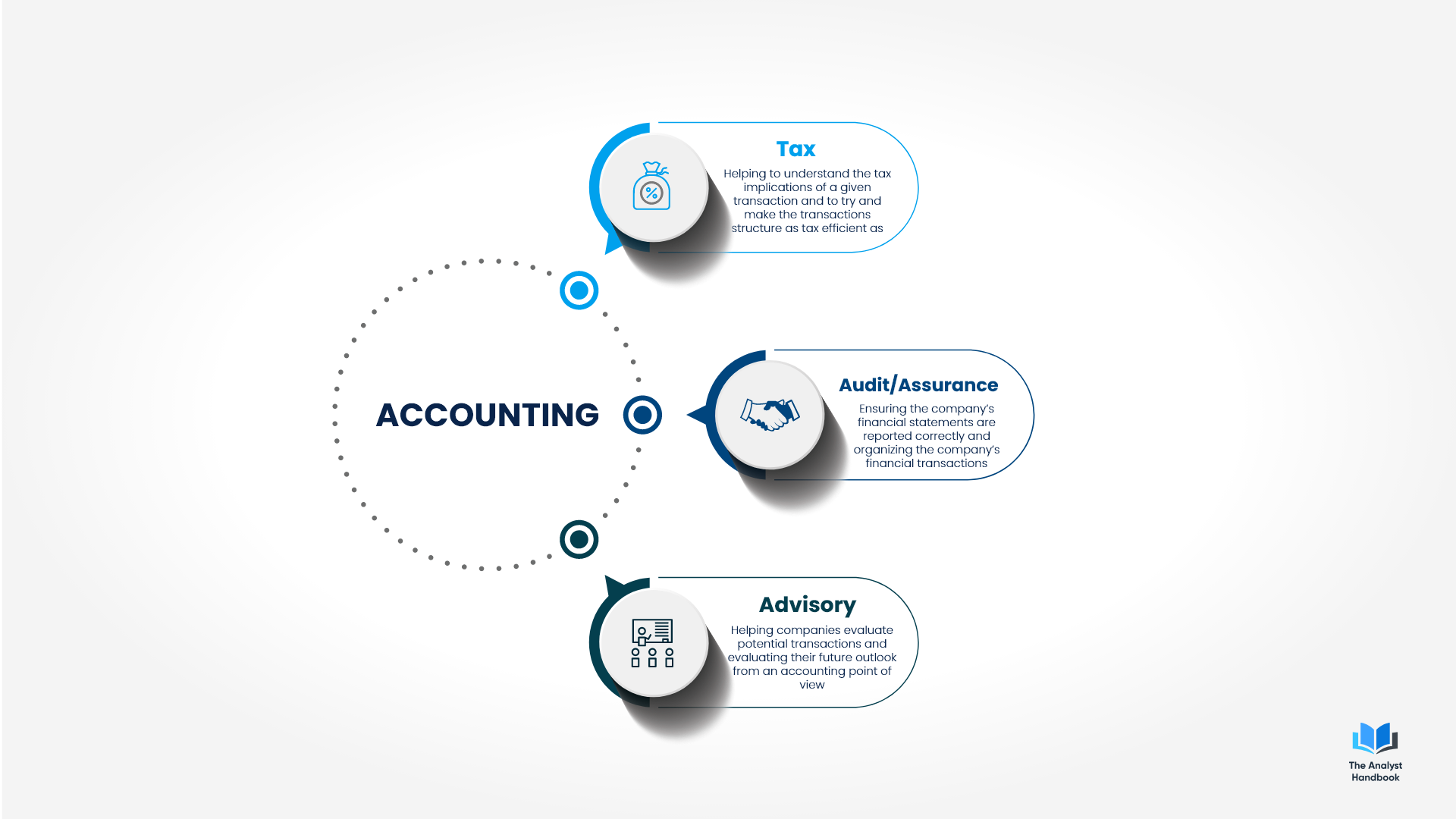
Accounting
Every business has a need for accounting and keeping the books or records in order. Most students come out of school with an Accounting degree and go to one of the big accounting firms.
Tax: You’ll primarily be dealing with how companies will be taxed in certain deals, transactions or situations. You’ll be working on understanding the tax implications behind the company’s operations or transactions. The goal of tax is to make the transaction or operations as tax efficient as possible and try to reduce the amount of taxes a company pays while still being compliant.
Audit/Assurance: You’ll be working with companies’ financial statements to ensure they are correct and in compliance with the necessary guidelines and policies. You’ll be making sure the financials are prepared in the correct manner and format depending on the accounting policies, corporate structure, and on the location of the company
Advisory: You’ll be advising companies on deals or transactions from an accounting point of view. Here you’ll be evaluating companies’ financials and trying to understand the company’s operations or future projections depending on the market conditions and outlook. You’ll be giving a recommendation or opinion on the transaction or deal from an accounting point of view.
Management Consulting: Working on behalf of a third-party consulting company that is engaged to help turn a company or business around based upon the management of the operations. Most often brought in when a company is struggling or needs help to become more profitable or efficient in their operations.
Technology Consulting: Working on behalf of a third-party technology company brought in to help another company or business with their technologies design, data, development, or infrastructure. Deals with making a company or business more technologically savvy or effective in its operations.
Strategy Consulting: Working on behalf of a third-party company engaged to help give a company direction or to help make a critical decision on behalf of the company. Help to give companies perspective, their experience, recommendations, and market information.
Risk and Compliance Consulting: Working on behalf of a third-party company brought in to help a company or business comply with the standards and regulations involving the company’s operations. Ensure a company is operating correctly, and within the confines of the law or their industry (or the industry a company plans to enter).
Marketing Consulting: Working on behalf of a third-party marketing company to help give companies and businesses advice on how to create effective marketing campaigns or properly market their products/services. Possibly to help companies evaluate their target audiences and promote their product in the most effective way possible. Often helping to create communities, audiences, and customers based on the messaging the company displays to the public through its marketing channels.
Human Resources Consulting: Working on behalf of a third-party human resources company to help company’s or businesses with their human resources departments or situations. Company’s or businesses will sometimes outsource their HR to another company or separate entity.
It’s also possible for a HR consultant to be engaged to help structure or reorganize a company’s human resources department.
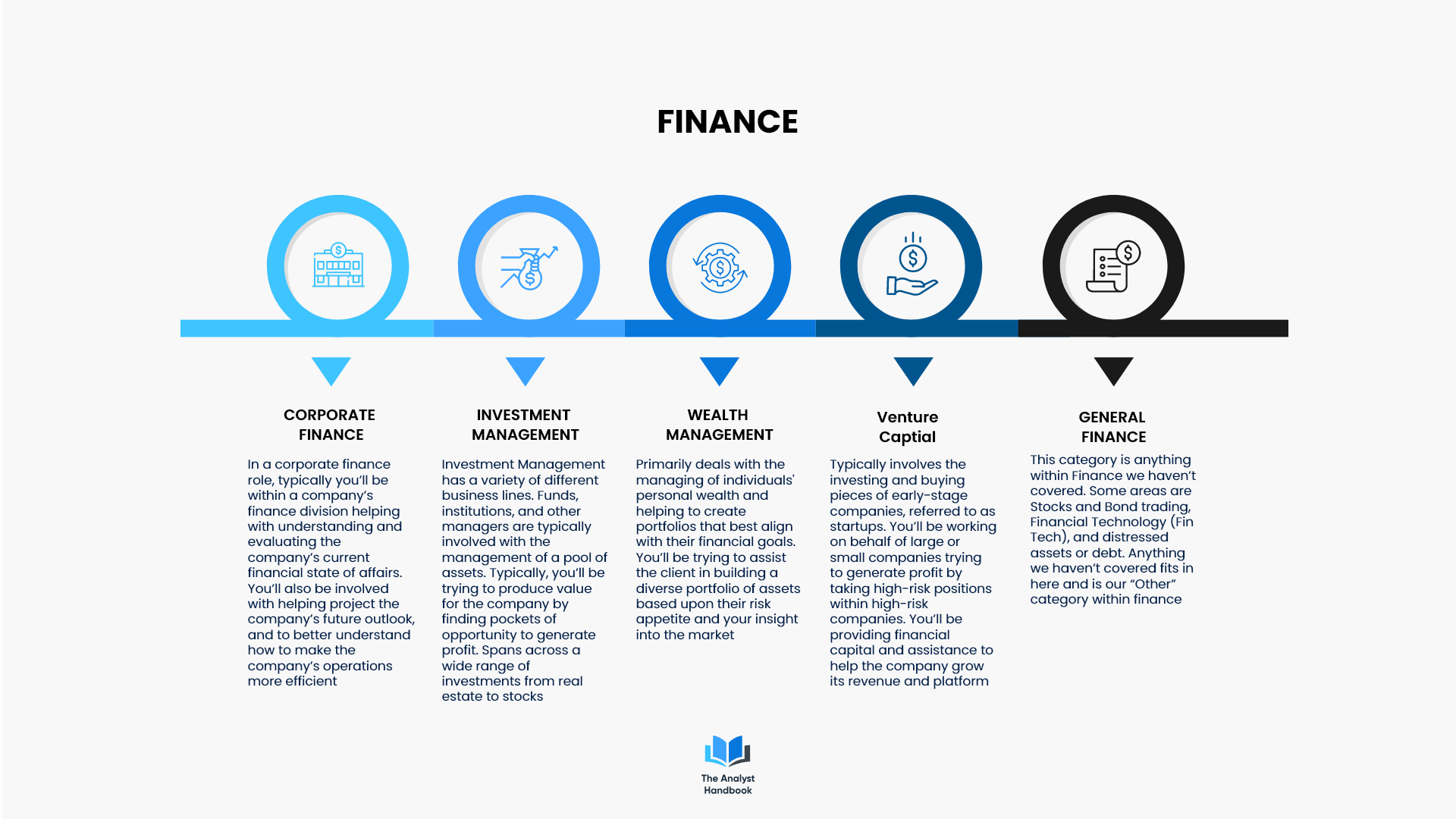
Finance
The world of finance is a complex arena, that has many angles, industries, and opportunities for you to become an Analyst in. Corporate Finance: Working in or on behalf of a company’s finance department. Primarily involved in the company’s financials, operations, and future projections. Projects might involve partnerships, analysis, and other finance-related projects.
Investment Management
Asset Management: Working on behalf of a financial institution to help manage, sell, or evaluate financial assets, investments, or instruments. Often times you'll be managing capital and helping to assist in its deployment.
Equity Research: Working primarily on researching and understanding companies financials and their future outlook. Providing recommendations or insight into how a company is performing and will perform in the future. Primarily divided by asset classes, company groups, or industry groups.
Sales & Trading: Working primarily in the sales and trading of securities within a fund or a financial institution. Acting upon research, and investment theses to help generate a profit within the public or private markets. Usually situated on a sales and trading floor with a large group of traders and monitors trying to understand and evaluate the current state of the macro or micro-economy to predict the future direction of a security or investment, then buying, selling, and trading based upon that intel.
Wealth Management: Working primarily on dealing with individuals' personal wealth and investment portfolios. Helping people manage their money and meet their financial goals. It usually involves a senior manager or director and a book or clientele of people’s assets to manage.
Venture Capital: Primarily involved with investing in early-stage companies and evaluating their potential for future growth. Most likely will be participating in funding rounds or helping companies grow their businesses and increase their valuations. Typically see large returns via exit, or losses from failure to execute their business plan. High risk, high reward industry.
General Finance: The grey area and any area of finance that hasn’t been covered. This is our “Other” category. Anything finance related that does not fall into one of the areas we’ve covered. Some examples are the trading and brokering of stocks and bonds. Other examples are distressed assets, financial technology, and anything else finance-related we haven’t covered.
Conclusion
Either way, you get to determine your own destiny, and the path you take. Use this to help guide you in understanding the different options available to you as an Analyst, or as an aspiring Analyst. Crush your Analyst position and rise up the ranks. Life’s a journey, map out your ride, and then enjoy it.
Mapping your career is very difficult especially early on. Often times we think or know the path we are going to take and end up on a totally different one. This guide is here to help define the different industries and areas most Analysts tend to pursue. A lot of companies will operate in several of these areas and will have a lot of overlap in the industries we touched upon. This is here to help you answer the questions you may have regarding an industry or sub-industry you may choose to pursue